Biodegradable and Compostable What's the Difference?

Biodegradable & Compostable Bags | Torise Environmental Solutions

Torise Biomaterials: Professional manufacturer of compostable bags
Support the environment: Every Torise bag you choose helps reduce plastic pollution.
Biodegradable bags vs. compostable bags: What is the difference?


Difference between compostable and biodegradable: what you need to know
What does biodegradable mean?
A biodegradable material is one that is able to decompose naturally in the environment under the action of microorganisms such as bacteria or fungi. However, this term is broad and does not specify how long it takes to decompose or the type of waste produced. So even if something is biodegradable, it may not be sustainable if the process takes years or leaves toxic residues.
What does compostable mean?
Compostable materials, on the other hand, are not only biodegradable, but they meet stricter criteria:
●They decompose within a specific time.
●They produce environmentally safe byproducts, such as compost or natural fertilizer.
●They require controlled conditions, such as those found in a factory or home composter.

Main differences between biodegradable and compostable bags
Although biodegradable and compostable bags are usually made from similar raw materials, they are not the same.
✔First, biodegradable bags degrade under natural conditions, while compostable bags need to be artificially composted under specific conditions.
✔The decomposition time of biodegradable bags in the natural environment is unpredictable, while compostable bags usually decompose within 6 months in industrial composting facilities or 12 months in home composting.
✔In addition, the certification standards are different: biodegradable bags do not need to prove that they are completely harmless after degradation, while compostable bags must prove that they are non-toxic after decomposition.
✔The term "compostable" is usually regulated and ensures that the material decomposes within a specified time and conditions, while "biodegradable" is less specific and can be interpreted more broadly.
Conclusion
While biodegradability ensures that the material will decompose naturally, composting goes a step further and ensures that the process is quick and beneficial to the environment. In situations where the necessary conditions for composting can be met, choosing compostable materials is a more sustainable choice.
Certifications for compostable bags
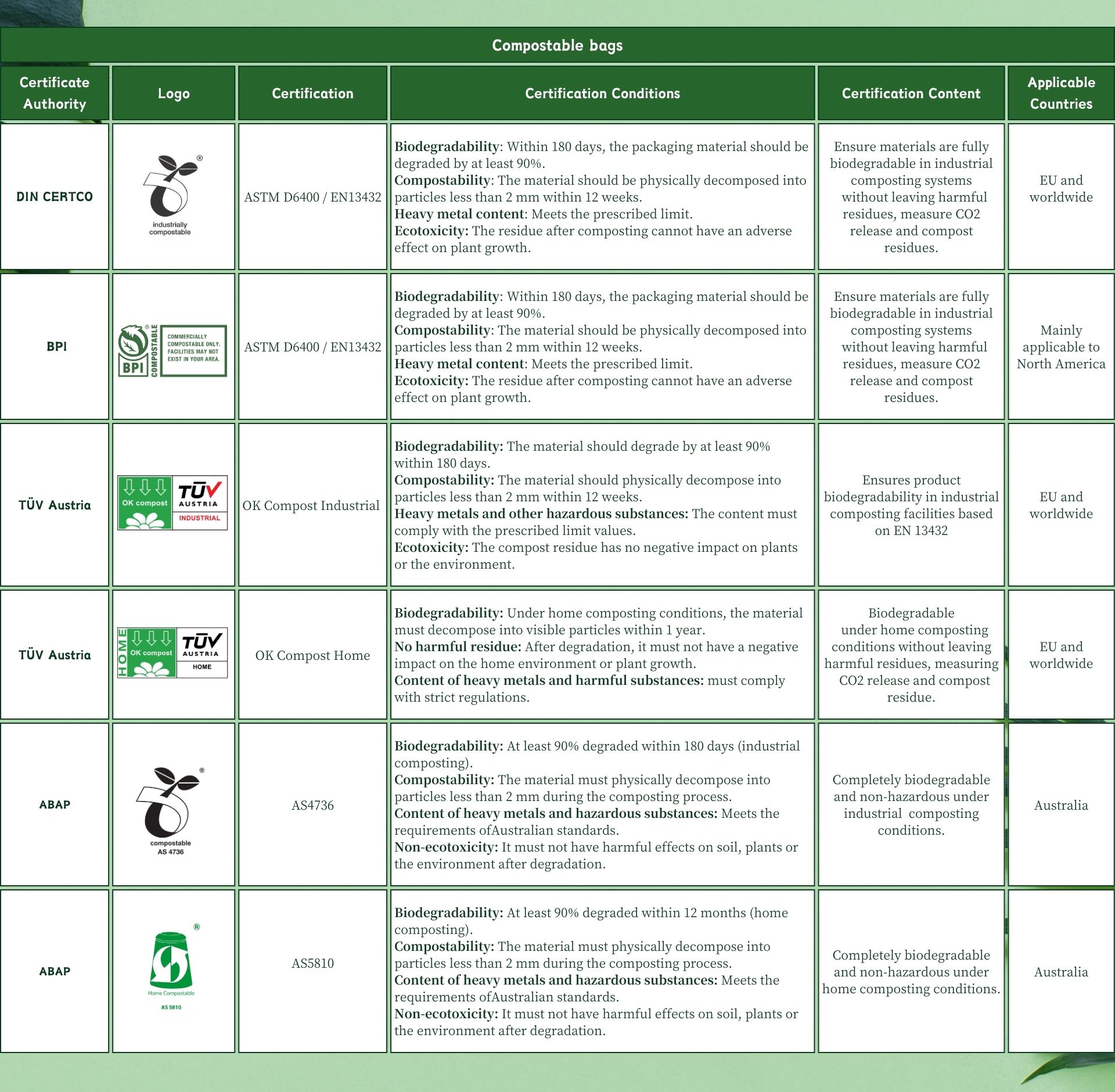
Worried about buying fake compostable bags?
Here are some ways to tell if your compostable bags are genuine:
Smell: Genuine biodegradable and compostable bags are usually odorless or have a light grain smell.
Feel: These bags are usually silky smooth, but if PBAT is added, they may feel slightly harder.
Color: Due to the characteristics of bio-based materials, it is difficult to make these bags completely transparent, so they usually look translucent or milky.
Have questions about how to identify truly compostable bags? Contact us and our team of experts will help you choose truly sustainable products.
Torise Biomaterials: A Trustworthy Partner in Environmental Protection
Products Certifications
Join us and contribute to a sustainable future for our planet by using Torise's compostable bags.

- Name:
- Sales Team
- Tel:
+86-18151919890
+86-0511-85598456
- Email:
- sales@torisegroup.com
- Address:
- Bio based industrial zone, Nanle County , Puyang , Henan , China

















