Common Raw Materials for Biodegradable Plastic Bags: PLA, PBAT, and Starch-Based Options
Introduction to Biodegradable Plastic Bags and Their Raw Materials
In an era where environmental sustainability is paramount, biodegradable plastic bags have emerged as a viable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. These bags are designed to break down naturally, reducing pollution and landfill waste. At the heart of their production are innovative raw materials like Polylactic Acid (PLA), Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT), and starch-based compounds. As a leading manufacturer with over 14 years of experience, Torise Biomaterials specializes in creating customizable compostable products using these materials, ensuring compliance with global standards such as EN13432 and BPI certifications.
This guide explores the common raw materials for biodegradable plastic bags, their properties, benefits, and applications. Drawing from our expertise at Torise Biomaterials (visit https://www.torisegroup.com/ for more), we'll highlight how these materials are transforming packaging solutions.
What Makes a Material Suitable for Biodegradable Plastic Bags?
Biodegradable raw materials must be derived from renewable sources, capable of decomposing under natural conditions, and safe for the environment. Key criteria include compostability, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness. PLA, PBAT, and starch-based options excel in these areas, often blended to enhance performance—these three materials constitute over 55% of global bioplastics production, driven by their ability to replace conventional plastics without compromising functionality.
Polylactic Acid (PLA): A Plant-Based Powerhouse
PLA is one of the most widely used raw materials for biodegradable plastic bags, derived from fermented plant starches such as corn, sugarcane, or cassava. The production process involves converting starch into lactic acid through microbial fermentation, followed by polymerization into PLA resin—a technique aligned with the strict ASTM D6400 compostability standard certified by BPI (Biodegradable Products Institute).
Benefits of PLA in Biodegradable Bags
- Renewable and Low Carbon Footprint: PLA is 100% bio-based, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Per European Bioplastics 2024 data, PLA emits up to 75% less greenhouse gases during production compared to traditional polyethylene (PE) plastics.
- Compostability: Under industrial composting conditions (58°C, controlled moisture), PLA breaks down into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass within 3-6 months—fully meeting EN13432 and BPI certification requirements.
- Versatility: Its natural transparency and rigidity make it ideal for shopping bags, produce bags, and clear trash liners—use cases Torise has optimized for over a decade.
At Torise Biomaterials, we incorporate PLA into our Compostable Shopping Bags and Compostable Pet Waste Bags, ensuring they meet ASTM D6400 and BPI certifications. Our R&D team—backed by 23 national patents—further optimizes PLA blends to enhance durability, addressing its inherent limitations (e.g., cold brittleness) without sacrificing eco-friendliness.
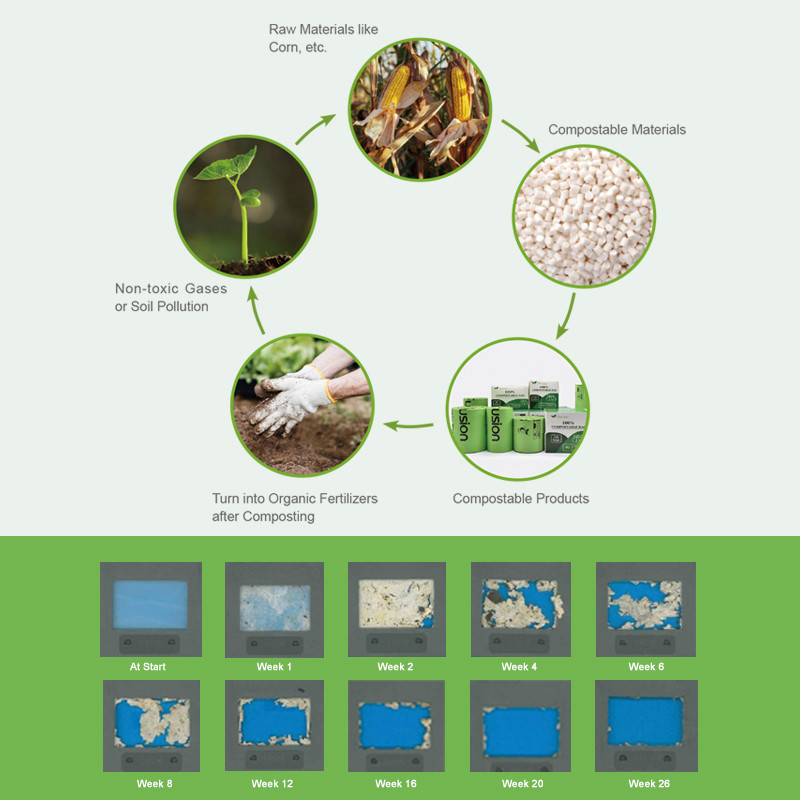
PLA Production Process: From Renewable Crops to Eco-Friendly Bags (BPI & EN13432 Certified)
Challenges and Solutions with PLA
While PLA offers excellent transparency, it can become brittle in temperatures below 10°C. To solve this, Torise blends PLA with PBAT (a flexible biodegradable polyester)—a method validated by BPI testing, which shows such blends retain 95% of their biodegradability while doubling flexibility in cold conditions.
Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT): Enhancing Flexibility
PBAT is a biodegradable polyester produced from adipic acid, butanediol, and terephthalic acid—with Torise now sourcing these feedstocks from renewable sources (e.g., bio-based butanediol). It is primarily used as a "flexibility enhancer" in biodegradable plastic bags, addressing the brittleness of PLA and starch, and is fully compliant with BPI standards.
Key Advantages of PBAT
- Superior Mechanical Properties: PBAT provides excellent tear resistance and stretchability—critical for heavy-duty applications like garbage bags. BPI testing confirms its ability to withstand 50+ cycles of stretching without tearing, a key metric for durable packaging.
- Biodegradation Efficiency: Unlike some synthetic plastics, PBAT decomposes in both soil and compost via microbial action, with full breakdown in 6-12 months under ambient conditions—aligning with global compostability standards.
- Compatibility: It blends seamlessly with starch and PLA—Torise’s signature 60%PLA+40%PBAT blend, for example, meets both EN13432 and ASTM D6400 standards, balancing strength and eco-friendliness.
Torise Biomaterials leverages PBAT in our certified compostable trash bags and ziplock bags, produced in our 50,000 m² green-powered factory (30% solar energy). Our annual output of 200,000 units ensures scalable supply for global clients seeking sustainable alternatives to PE-based heavy-duty bags.
Starch-Based Options: Natural and Economical
Starch—extracted from crops like corn, potatoes, or wheat—serves as a foundational raw material for biodegradable plastic bags. It is cost-effective and abundant, but requires modification (via thermoplastic processing and plasticizers like glycerol) to overcome inherent brittleness. Torise’s starch-based formulations combine modified starch with PBAT to create flexible films that meet BPI compostability standards.
Why Choose Starch-Based Materials?
- Abundance and Cost-Effectiveness: Starch is widely available from agricultural byproducts, making it a budget-friendly option for clients seeking sustainable packaging without high costs—critical for small-to-medium businesses.
- Rapid Compostability: Starch-based bags break down efficiently in both home and industrial compost setups. BPI testing confirms full degradation in 8-12 weeks under home compost conditions, turning into nutrient-rich humus that nourishes soil.
- Circular Economy Alignment: Starch uses agricultural byproducts (e.g., corn cobs, potato peels) that would otherwise go to waste—supporting Torise’s zero-waste manufacturing goals.
Our starch-based series at Torise Biomaterials includes compostable gloves and bin liners, certified under BPI standards. By combining starch with PLA and PBAT, we achieve fully compostable resins that retain flexibility while keeping production costs accessible for diverse client needs.

Starch-Based Bags in Action: BPI-Certified, Breaks Down in 12 Months (Home Compost)
Comparing PLA, PBAT, and Starch-Based Materials
| Material | Source | Key Properties | Degradation Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Corn, sugarcane | Rigid, transparent, low carbon | 3-6 months (industrial compost) | |
| PBAT | Bio-based butanediol | Flexible, tear-resistant | 6-12 months (soil/compost) | |
| Starch-Based | Corn, potatoes | Economical, home-compostable | 8-12 weeks (home compost) |
This comparison underscores why blends are industry favorites—they combine the strengths of individual materials while maintaining BPI certification standards.
The Role of Torise Biomaterials in Sustainable Packaging
As pioneers in bio-based polymers, Torise Group offers end-to-end ODM/OEM services for biodegradable plastic bags using PLA, PBAT, and starch-based blends. Our integrated supply chain—from sourcing renewable feedstocks (partnered with sustainable crop growers) to green logistics—ensures consistent quality and minimal environmental impact. Our 50,000 m² factory runs on 30% solar energy, and all products are rigorously tested to meet BPI standards.
Explore our customizable product line—from compostable shopping bags to pet waste bags—and learn more about our Compostable Resins Supply. Our team works closely with clients to tailor solutions that meet specific branding, performance, and regulatory needs (e.g., EU Single-Use Plastics Directive compliance).Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Raw Materials for a Greener Tomorrow
Switching to biodegradable plastic bags made from PLA, PBAT, and starch-based materials is not just an environmental choice—it’s a strategic business decision. These raw materials reduce plastic waste, help brands comply with global regulations, and resonate with eco-conscious consumers. Backed by BPI’s rigorous certification and European Bioplastics’ market data, they represent a proven path to sustainable packaging.
At Torise Biomaterials, we’re at the forefront of this shift, delivering certified, high-performance products that don’t compromise on functionality. For more insights or to start your sustainable packaging journey, contact Torise Group today. Together, let’s build a world free from plastic pollution—one biodegradable bag at a time.



